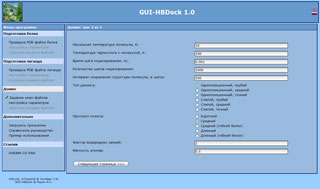
General layout of GUI-HBDock program in a web browser window. Docking calculation parameters' setup page.
The HBDock program is designed for computation tasks with three-dimensional protein and nucleic acid structures developed for searches of low molecular ligands' docking sites. It can perform both blind and single-position docking with a configurable precision. The main feature of the original blind docking method is a hierarchical algorithm. The first stage of the algorithm performs a full search and ranging by significance of all cavities, pockets, and grooves as potential binding sites on a molecular surface of a biopolymer under consideration. The second stage of the algorithm performs a detailed docking of a ligand for the most significant binding sites by global optimization using a molecular dynamics method with a thermal annealing and a controllable deformation of potential energy surface of protein-ligand complex. The online version GUI-HBDock has been developed. It enables to form a task as a single executable file, export that file to the client side and ensure its execution. The GUI-HBDock program is designed to check protein and ligand files, and to create control files for the HBDock program in an interactive mode. The program also creates a command file (for Microsoft Windows® and Linux operating systems), that allows to start computations on the client site immediately. Operating system is detected automatically, that allows users not to think of operating system specific tweaks. The GUI-HBDock program has a complete support of all wide-spread web browsers, and its interface supports English and Russian languages. A reference manual and links for HBDock download are available at the program's web site.
The HBDock program was tested on huge series of protein-ligand complexes and proved its superiority in reliability. The rate of successful docking is equal to 86%, so far as the most cited commercial programs have no more than 75% ratio of successful docking.
The HBDock program has been used to construct a ligand inhibitor of RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus. A variant of inhibitor with the maximum binding energy is constructed by varying side groups in an α,γ-biketoacid base.
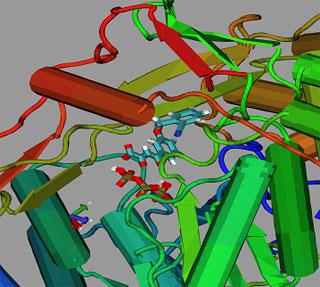
An inhibitor model variant, bound to the RNA polymerase active site of a hepatitis C virus.
If you use the HBDock, or GUI-HBDock, or both programs in any work distributed or published, please include the following reference:
(not published yet)
Links on the topic: